Pips are the units used to measure movement in a forex pair. A forex pip usually refers to a
movement in the fourth decimal place of a currency pair. So, if
EUR/USD moves from $1.35361 to $1.35371, then it has moved a single pip. The decimal places
that are shown after the pip are called micro pips, or
sometimes pipettes, and represent a fraction of a pip.
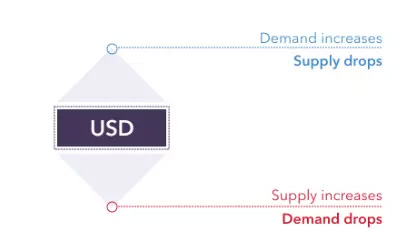
Like most financial markets, forex is primarily driven by the forces of supply and demand,
and it is important to gain an understanding of the influences that
drive these factors.
Central banks
Supply is controlled by central banks, who can announce measures that will have a
significant effect on their currency’s price. Quantitative easing, for instance,
involves injecting more money into an economy, and can cause its currency’s price to
drop.
Central banks also control the base interest rate for an economy.
If you purchase an asset in a currency that has a high interest rate, you may get higher
returns. This can make investors flock to a country that has recently
raised interest rates, in turn boosting its economy and driving up its currency.
However, higher interest rates can also make borrowing money harder. If money is more
expensive to borrow, investing is harder, and currencies may weaken.
News reports
Commercial banks and other investors tend to want to put their capital into economies
that have a strong outlook. So, if a positive piece of news hits the
markets about a certain region, it will encourage investment and increase demand for
that region’s currency.
Unless there is a parallel increase in supply for the currency, the disparity between
supply and demand will cause its price to increase. Similarly, a piece of
negative news can cause investment to decrease and lower a currency’s price. As a
result, currencies tend to reflect the reported economic health of the
country or region that they represent.
Take a look at our economic calendar to see what’s ahead, and pay particular attention to:
Inflation figures
GDP
Production reports
Retail sales
Employment
Market sentiment
Market sentiment, which is often in reaction to the news, can also play a major role in
driving currency prices. If traders believe that a currency is headed in
a certain direction, they will trade accordingly and may convince others to follow suit,
increasing or decreasing demand.
You can see sentiment from IG Option clients – as well as live prices and fundamentals –
on our market data pages for each market.




 © 2019-2024
© 2019-2024